Joint work with Alonso Alfaro-Ureña. Revision solicited (R&R) at the American Economic Journal: Microeconomics.
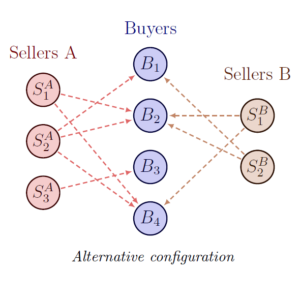 Abstract. This paper develops a framework for the empirical analysis of the determinants of input supplier choice on the extensive margin using firm-to-firm transaction data. Building on a theoretical model of production network formation, we characterize the assumptions that enable a transformation of the multinomial logit likelihood function from which the seller fixed effects, which encode the seller marginal costs, vanish. This transformation conditions, for each subnetwork restricted to one supplier industry, on the out-degree of sellers (a sufficient statistic for the seller fixed effect) and the in-degree of buyers (which is pinned down by technology and by “make-or-buy” decisions). This approach delivers a consistent estimator for the effect of dyadic explanatory variables, which in our model are interpreted as matching frictions, on the supplier choice probability. The estimator is easy to implement and in Monte Carlo simulations it outperforms alternatives based on group fixed effects. In an empirical application about the effect of a major Costa Rican infrastructural project on firm-to-firm connections, our approach yields estimates typically much smaller in magnitude than those from naive multinomial logit.
Abstract. This paper develops a framework for the empirical analysis of the determinants of input supplier choice on the extensive margin using firm-to-firm transaction data. Building on a theoretical model of production network formation, we characterize the assumptions that enable a transformation of the multinomial logit likelihood function from which the seller fixed effects, which encode the seller marginal costs, vanish. This transformation conditions, for each subnetwork restricted to one supplier industry, on the out-degree of sellers (a sufficient statistic for the seller fixed effect) and the in-degree of buyers (which is pinned down by technology and by “make-or-buy” decisions). This approach delivers a consistent estimator for the effect of dyadic explanatory variables, which in our model are interpreted as matching frictions, on the supplier choice probability. The estimator is easy to implement and in Monte Carlo simulations it outperforms alternatives based on group fixed effects. In an empirical application about the effect of a major Costa Rican infrastructural project on firm-to-firm connections, our approach yields estimates typically much smaller in magnitude than those from naive multinomial logit.